



The separator is located on the P3 beam in the target chamber and is usually configured for a proton beam. The beam of mono-energetic protons impacts to the 1 mm thick tungsten target, where the Rutherford scattering takes place. The scattered protons have wide energy spectrum due their scattering (RBS) in the depth of the target, up to the maximum energy that corresponds to proton RBS on tungsten target at given angle.
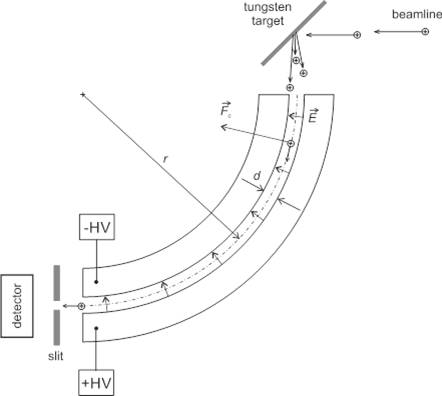 FIG. 1: Schematic diagram of electrostatic separator.
FIG. 1: Schematic diagram of electrostatic separator.
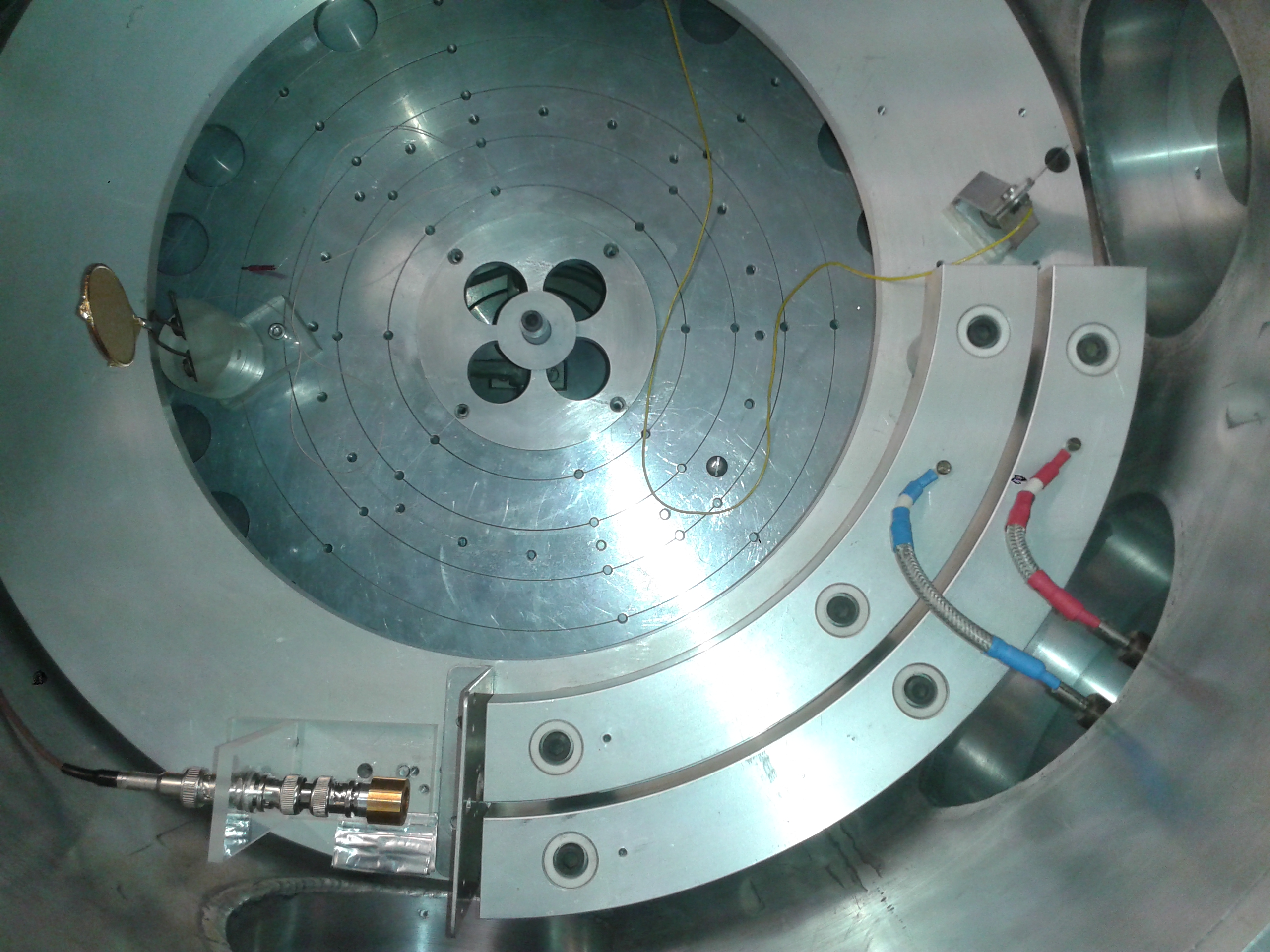 FIG. 2: Photography od the electrostatic separator in the vacuum chamber.
FIG. 2: Photography od the electrostatic separator in the vacuum chamber.
A part of scattered protons enters a thin arc aperture of the electrostatic separator. This aperture is created by long arc electrodes. On one of them the positive voltage +U is connected, on the other one there is the negative high voltage –U. We use two HV sources with a common ground. We can set the voltage up to ±10,0 kV at sources. The electrostatic (centripetal) force affects the protons in the aperture and they move on circular trajectories. Their radius depends on the speed (energy) with which protons enter the separator. Only the protons with energy that complies with separator conditions pass through the separator. This voltage determinates the amount of electrostatic force. Consequently, the kinetic energy of separated protons is T(keV) = 40·U(kV).
The accelerator and the laboratory are operated and upgraded in frame of the research funding grant "VdG Research infrastructure" by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic (Contract No. LM2015077).
Last update: January 2021